Last Updated on
Frequency weighting is an important factor to occupational noise measurements.Frequency weightings are used to represent sound levels (measurement unit in decibel (dB)).
For example, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recommends exposure limit of 85 dBA in a 8-hour work shift. The letter ‘A’ shows the frequency weighting filter applied to the measured sound.
The Importance of Frequency Weightings
When measuring sound pressure level especially for potentially damaging noise levels at workplace, it is crucial that the sound level meter is able to accurately monitor noise as what the human ear actually hears. In order to represent the human hearing precisely, frequency weightings is used by putting more weight into some frequencies over others.
Different Noise Frequency Weightings
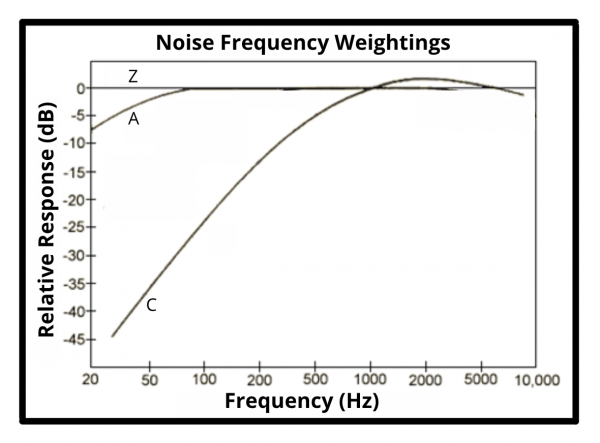
Different noise frequency weightings contains different range of noise frequency related to the human ear. There are 6 kinds of noise frequency weightings; A-,B-,C-,D-,G- and Z-weightings.
A-, C-, and Z-weightings are the most commonly used nowadays as defined in the sound level meter standards IEC 61672:2013, while B- and D- weightings are no longer mandatory to use.
‘A’, ‘C’ and ‘Z’ weightings
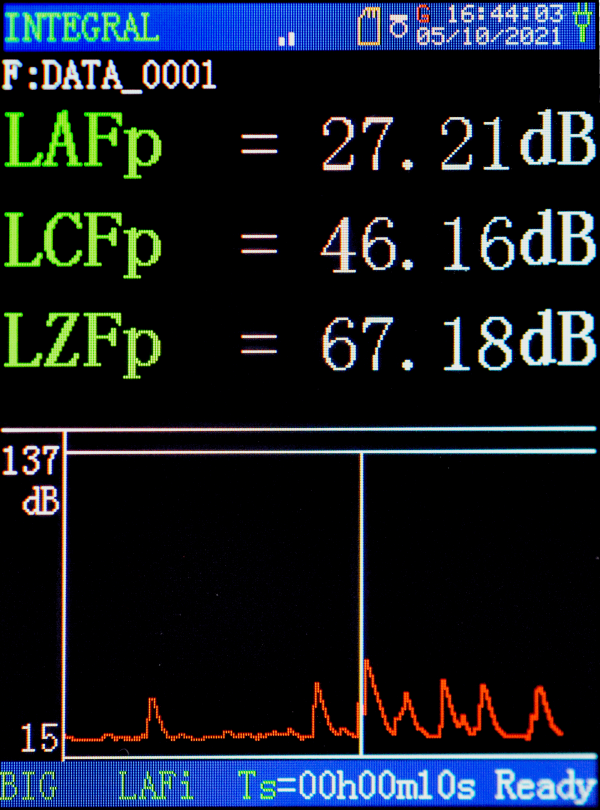
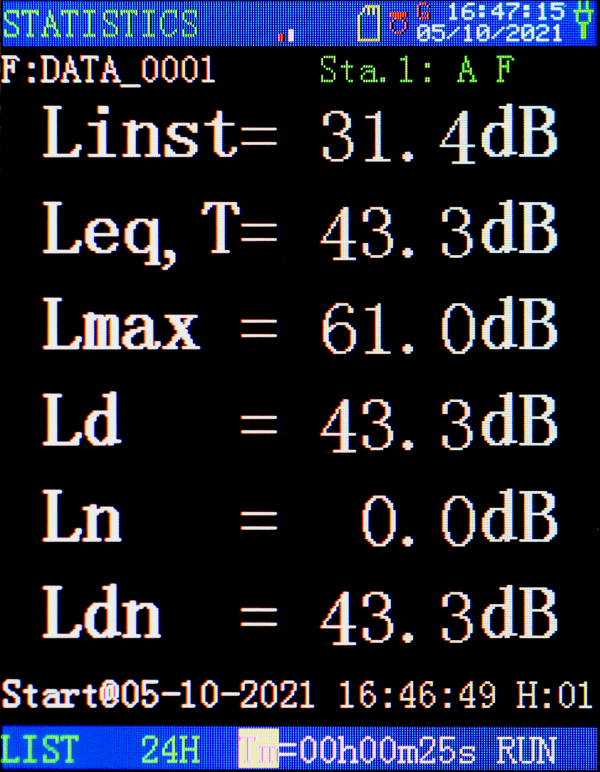
The screenshots below from ST-15D Sound Analyzer shows the Sound Pressure Level (SPL), with the maximum and minimum sound level (Lmax and Lmin) with a choice of A, C, and Z frequency weightings.
A – Weighting
The A weighting is the most commonly used frequency response and best reflects the sensitivity of the human ear to noise. The A weighting filter covers the full noise frequency range from 20Hz to 20kHz.International standards such as the IEC 61672 and ANSI S1.4. (USA) require to at least include an A-weighting filter in sound level meters. The A weighted frequency curve is mandatory for environmental and industrial noise measurement as well as evaluating potential hearing damage and health effects of noise.
Measurements are usually displayed as dB(A) or dBA or as LAeq, LAFmax, LAE. The A indicates for the A-weighting.
C – Weighting
The C weighting are typically used for higher peak noise level measurements such as Peak Sound Pressure Measurements which referred as CPeak. The C-weighted measurements is ideal for monitoring short spontaneous loud noises such as explosions, bangs, high power engines, explosions, etc.
Measurements are displayed as dB(C) or dBC, LCeq, LCPeak, LCE. The C indicates for the C-weighting.
Z – Weighting
The Z weighting is made with zero weighting for the human ear which covers flat frequency response of 8Hz to 20kHz (+/- 1.5dB). This is often used in octave band analysis and for measuring environmental noise.
Measurements are displayed as dB(Z) or dBZ, or LZeq, LZFmax, LZE. The Z indicates for the Z-weighting.
Most modern and advanced sound level meters and sound analyzers will have A-,C-,Z- weightings.