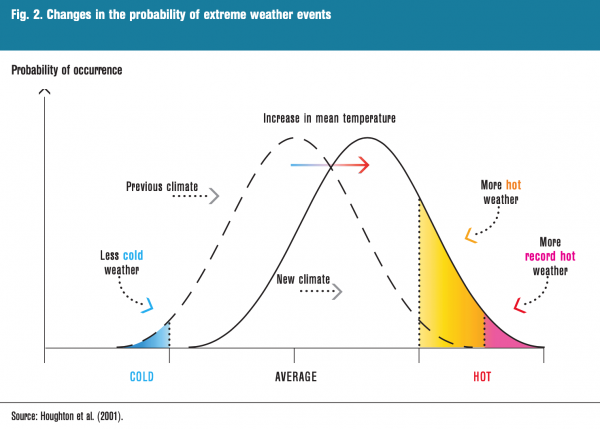
What is Heatwave?
In simple words, heatwave is abnormally high surface temperatures resulting in a heat and hot weather that can last for several days or weeks. The World Meteorological Organization defines it as five or more consecutive days during which the daily maximum temperature surpasses the average maximum temperature by 5 °C (9 °F) or more. Some countries have adopted their own standards.
Heatwaves are one of the most life-threatening natural hazards. Heatwaves can cause heath-related illness and deaths. Moreover, it can also cause infrastructure problems such as water drainage and power blackouts.
Historically, on average, there is at least one heatwave phenomenon happening each year around the world. Here are the top 5 most extreme heatwaves around the world:
- U.S. heatwave – California,1913
- Recorded high temperature: 57 °C (134 °F) at Furnace Creek, also known as the highest ambient air temperature recorded on Earth.
- European heatwave – 2003
- In summer 2003, a record high temperature of 47 °C (117 °F) covered across Europe.
- Number of death: more than 30,000 people
- Indian heatwave – 2015
- According to the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), a heat wave is qualified when air temperatures of at least 40 °C (104 °F) in the plains or greater than 30 °C (86 °F) in the hilly regions. For the IMD classification of heat waves, temperatures greater than 46 °C (114.8 °F) are considered and classified as severe heat waves
- Number of death: more than 2,500 people
- Australia heatwave – Victoria & Melbourne, 2009
- Recorded high temperature: 40 °C (104 °F) in Adelaide for six days in a row. Many rural areas experienced temperatures around 45 °C (113 °F). While in Victoria, Melbourne for three consecutive days the temperature was recorded over 43 °C (109 °F), and also recorded its highest ever temperature 8 days later in a secondary heatwave, with temperatures peaking at 46.4 °C (115.5 °F).
- During this heat wave Victoria suffered from large bushfires (Black Saturday Bushfires) which killed 173 people and destroyed more than 2,500 homes.
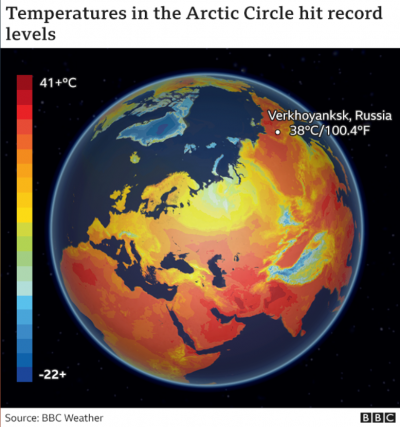
- Russian heatwave – Verkhoyansk, 2020
- Recorded high temperature: 38 °C (100.4 °F) at Verkhoyansk, Siberia, Russia, which is part of the Arctic Circle, where temperatures normally as cold as -60 °C.
The Health Impact of Heatwave
The impact of heatwave on health mainly depends on the intensity and the duration of the temperature. Prolonged exposure to extreme heat can cause dehydration, exhaustion and faintness. When the temperature is too hot and the body no longer can adapt to the high temperatures it may cause heat-related illness such as heat stroke.

Each person body’s reactions to heat is different. However, older people, children, and people with underlying chronic diseases are at a greater risk of complications and death during a heatwave. Therefore, it is important to always stay alerted with the health and safety recommendations of local authorities.
Some doable tips during heatwave:
- Stay in air-conditioned room
- Avoid direct sunlight
- Drink plenty of water
Managing Workplace Safety with TWL-1S Heat Stress Meter
Managing heat stress in the workplace is possible with Scarlet’s TWL-1S Heat Stress Meter. The TWL-1S is a heat stress management device that gives clear instructions for labor, rest, and hydration plan. The device is designed using a thermal work limit(TWL) algorithm, which according to study found to be better than the commonly used Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WGBT), since TWL considers a more comprehensive factors affecting heat impact including the direct measurement of wind, work rate, even clothing factor.
TWL-1S can be used indoor or outdoor to assess thermal risk level in various work sites such as construction sites, factories, mining port, etc.
Watch the video below to learn more about the TWL-1S.